Public Queue Management with Facial Recognition Using Computer Vision
- Vathslya Yedidi
- February 5, 2025
Managing crowds efficiently and securely is a critical challenge for many public spaces, from large-scale events like concerts, festivals, and places of worship to transportation hubs and offices. Traditional methods often struggle to cope with the volume and complexity of modern gatherings, leading to long wait times, security vulnerabilities, and, in extreme cases, crowd disasters like stampedes.
Recent incidents highlight better crowd and queue management solutions. In January 2025, a stampede at the Maha Kumbh Mela resulted in multiple fatalities as millions of devotees overwhelmed existing crowd control measures.
Similarly, at the Tirupati Temple, an uncontrolled surge of worshippers led to at least six deaths and dozens of injuries. Despite CCTV surveillance, these tragedies demonstrate that traditional crowd-monitoring solutions are insufficient.
Facial recognition using Computer Vision for public queue management provides a better solution to these challenges by automating entry and exit processes, offering real-time crowd insights, and enhancing security. Queue management also involves real-time tracking of devotees and visitors to monitor movement patterns and manage crowd flow dynamically, along with surveillance-driven security to detect risks before they escalate.
This blog explores how facial recognition, real-time tracking, and surveillance-driven security enhance public queue management, examining their benefits, addressing privacy concerns, and showcasing real-world implementations.
Challenges in Public Queue Management: The Need for an Advanced Approach
Public events and places of worship frequently draw massive crowds, making queue management a critical operational concern. Traditional methods, relying on manual checks, physical barriers, and static queuing systems, often struggle to deliver efficiency, security, and a positive attendee experience. This leads to a range of challenges:
- Prolonged Wait Times and Inefficiencies: Manual ticket verification, ID checks, and security screenings create bottlenecks at entry points, causing frustration and congestion. Peak hours at religious sites or large events exacerbate these issues, impacting visitor’s experience and operational flow.
- Lack of Real-Time Queue Monitoring: Traditional queuing systems cannot track queues in real time, hindering the prediction and management of crowd movement. Event staff struggle to address bottlenecks effectively and guide attendees to available entry points without automated queue monitoring.
- Security Vulnerabilities: Reliance on manual security checks increases the risk of unauthorized access, ticket fraud, and security breaches. Ensuring only authorized individuals enter restricted zones is nearly impossible in large gatherings without automated identity verification.
- Limited Accessibility and Queue Personalization: Public queues often fail to adequately accommodate specific attendee needs, such as elderly worshippers, individuals with disabilities, or VIP guests. This lack of personalized queue management can lead to discomfort and inefficient entry processes.
- Minimal Data Insights: Traditional queue systems provide little to no data on entry times, visitor flow, or congestion points. Optimizing queue management becomes a reactive rather than proactive process without real-time and historical data.
- Scalability Challenges: As event sizes and religious congregations grow, traditional queue management methods struggle to scale effectively. The absence of automated tracking and AI-driven adjustments can lead to operational breakdowns, overcrowding, and inefficiencies in handling large numbers of attendees.
- Entry and Exit Tracking Issues: Traditional queue management systems lack real-time monitoring of individuals entering and exiting a venue, leading to inaccurate attendee counts, overcrowding, and security risks. Without an efficient tracking mechanism, unauthorized multiple entries can occur, making it difficult to control capacity and prevent safety breaches.

How Facial Recognition Using Computer Vision Improves Queue Management
Computer Vision-based facial recognition provides an automated, contactless, and data-driven approach to streamlining entry, tracking queue flow, optimizing crowd movement, and enhancing security.
1. Seamless, Secure, and Fast-Tracked Entry with Facial Recognition
Facial recognition eliminates ID verification, ticket scanning, and security screening inefficiencies by automating identity authentication and enabling fast, touchless, seamless entry processes.
- Pre-Registered Authentication: Visitors register their facial data in advance, allowing instant, hassle-free check-in upon arrival.
- Contactless Entry Gates: AI-powered cameras verify attendees in seconds, significantly reducing long queues and wait times.
- Multi-Point Access Control: The system synchronizes across multiple entry gates, preventing fraudulent re-entry or congestion.
- VIP & Special Access Processing: Facial recognition allows priority access for VIP guests, elderly visitors, or people with disabilities without manual intervention.
Use Case
At religious sites like Tirupati Balaji or Mecca, where footfall is high, automated entry gates powered by facial recognition can streamline access, ensuring smooth and fair queue movement while reducing waiting times.
2. Intelligent Queue Tracking for Crowd Flow Optimization
AI-powered systems track crowd density and movement, offering adaptive queue management solutions.
- AI-Powered Crowd Density Analysis: Cameras analyze queue length, waiting time, and movement to detect potential overcrowding before it happens.
- Automated Queue Adjustments: AI suggests dynamic rerouting of visitors to alternate entry points or waiting areas to prevent congestion.
- Smart Capacity Control: The system limits entry based on real-time occupancy data, ensuring controlled crowd distribution.
- Visitor Flow Analytics: Organizers can analyze historical queue patterns to optimize event planning for future gatherings.
Use Case
During large pilgrimages such as Kumbh Mela or Hajj, AI-powered surveillance predicts and prevents stampedes by monitoring crowd surges and redirecting foot traffic, ensuring safety and controlled movement.
3. Advanced Security and Unauthorized Access Prevention
Security concerns at large public events and religious gatherings require proactive monitoring. Facial recognition strengthens security by automating identity verification and detecting flagged individuals in real-time.
- Instant Identity Verification: The system grants access only to authorized visitors, reducing the risk of security breaches.
- Automated Watchlist Screening: AI identifies blacklisted or suspicious individuals and alerts security personnel immediately.
- Facial Recognition with Thermal Scanning: Integrating thermal cameras helps detect visitors with elevated temperatures, enhancing public health safety.
- Lost Individual Identification: The system helps locate missing children or elderly individuals in a crowd by scanning their facial data across live surveillance feeds.
Use Case
At large-scale public events like concerts, marathons, or political rallies, facial recognition using Vision AI ensures that only authorized ticket holders enter restricted areas, preventing unauthorized access and security risks.
4. Smart Exit and Re-Entry Management for Efficient Dispersal
Exit processes are just as critical as entry. Face detection using Vision AI automates exit tracking while preventing unauthorized re-entry, ensuring smooth dispersal of attendees.
- Automated Exit Validation: Visitors exit smoothly without manual security checks, reducing congestion at departure points.
- Controlled Re-Entry Tracking: Attendees who leave can only re-enter if authorized, eliminating manual ticket validation delays.
- One-Time Authentication Prevention: The system prevents ticket/pass reuse, ensuring visitors do not re-enter illegally using someone else’s credentials.
- Emergency Exit Planning: AI analyzes real-time foot traffic data to optimize emergency evacuation procedures if needed.
Use Case
At temples with time-based darshan slots, facial recognition ensures that once a devotee exits, they cannot re-enter using someone else’s credentials, maintaining fairness and efficient crowd control.
5. Data-Driven Insights for Future Optimization
AI-powered queue management provides invaluable data analytics that help organizers make informed decisions for future improvements.
- Peak Hour Analysis: Identify the busiest times and optimize entry/exit procedures accordingly.
- Visitor Demographics Tracking: Understand age groups, attendance trends, and return visitors for better event planning.
- Predictive Queue Modeling: AI predicts queue congestion based on historical data, allowing proactive queue management.
- Security Reports & Risk Assessments: Track security incidents, unauthorized access attempts, and overall event safety performance.
Use Case
Using facial recognition with Computer Vision analytics, large-scale religious sites and stadiums can refine their crowd management strategies for future events, ensuring a safer and more organized experience.
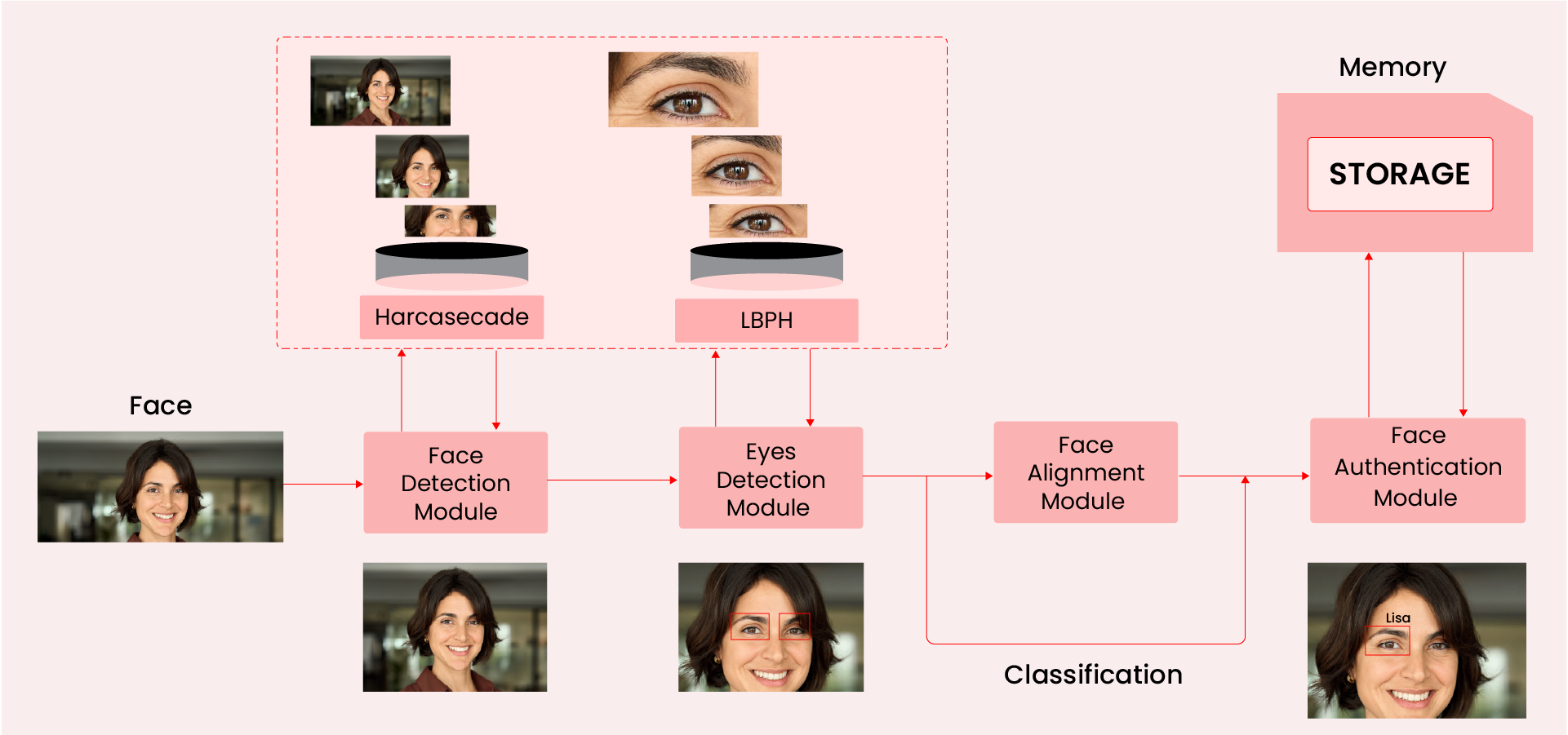
Applications Across Diverse Public Spaces in Queue Management
The benefits of facial recognition using Computer Vision extend across various public spaces as follows
- Large-Scale Events: Concerts, sporting events, festivals, and conferences benefit from faster entry, improved crowd control, and enhanced security, reducing wait times and maximizing safety.
- Places of Worship: Temples, churches, mosques, and religious sites can efficiently manage large influxes of worshippers, especially during peak events or holidays.
- Transportation Hubs: Automated identity verification can enhance security and streamline passenger flow at airports, train stations, and bus terminals.
- Offices and Public Services: Government service centers, courthouses, and public buildings can improve efficiency and citizen satisfaction by reducing wait times and optimizing resource allocation.
Addressing Privacy Concerns: A Responsible Approach
The use of facial recognition technology raises valid privacy concerns. Addressing these concerns proactively and implementing responsible data handling practices is crucial. This includes:
- Transparency: Informing individuals about how their data is collected and used. Open communication about data practices is essential for building trust.
- Consent: Obtaining explicit consent before collecting facial recognition data. Individuals should have the right to choose whether their data is collected.
- Data Security: Implementing robust security measures to protect sensitive information. Data must be protected from unauthorized access and misuse.
- Data Minimization: Collecting only the necessary data for the intended purpose. Limiting data collection minimizes the risk of privacy breaches.
- Data Retention: Limiting the retention of facial recognition data to a specific timeframe. Data should not be kept longer than necessary.
- Opt-out Mechanisms: Provide individuals with the option to opt out of facial recognition systems. Individuals should have control over their data.

Real-time AI Facial Recognition for Smarter Public Queue Flow Management
Several high-footfall venues have already begun implementing these technologies with significant success.
1. Mahakaleshwar Temple’s Technological Adoption
The Mahakaleshwar Temple in Ujjain has implemented AI-enabled facial recognition technology to manage crowds and ensure security. With 700 high-resolution CCTV cameras, the system aids in monitoring devotee influx and maintaining an organized worship experience.
2. Integration into Sports Stadiums
Intuit Dome, Los Angeles, opened in 2024. This $2 billion arena uses facial recognition to streamline entry, concessions, and access to various areas. Attendees can opt into the “Game Face ID” program, which allows for ticketless entry and cashless purchases, thereby reducing wait times and enhancing the fan experience.
Conclusion
Facial recognition using Computer Vision improves public queue management by making entry seamless, enhancing security, and optimizing crowd flow. From large-scale events and religious gatherings to transportation hubs, this approach ensures faster processing, better organization, and improved safety. As adoption expands, prioritizing responsible data practices will create more efficient and secure public spaces.
Want to implement AI-powered queue management for your venue? Contact us today to explore how facial detection using Computer Vision can enhance security, optimize crowd flow, and deliver seamless visitor experiences.

